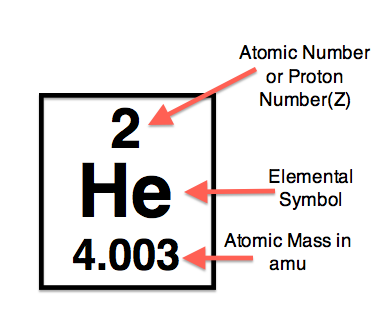
Gaseous chemical element, symbol: He, atomic number: 2 and atomic weight 4,0026 g/mol. Helium is one of the noble gases of group O in the periodic table. It’s the second lightest element. The main helium source in the world is a series of fields of natural gas in the United States. In its 1961 report, the Commission recommended Ar (He) = 4.0026 based on the atomic mass of 4 He to four decimal places. The abundance of 3 He in air of 0.000 137% as determined by Nier had a negligible effect on the atomic weight of helium. Helium is a chemical element with atomic number 2 which means there are 2 protons and 2 electrons in the atomic structure. The chemical symbol for Helium is He. The atom consist of a small but massive nucleus surrounded by a cloud of rapidly moving electrons. The nucleus is composed of protons and neutrons. A-The atomic number is greater. B-the atomic mass and and atomic number are equal. C-helium does not have an atomic number. D-the atomic mass is greater.
We remember from our school chemistry course that every element has its own specific atomic number. It is the same as the number of protons that the atom of each element has, so sometimes atomic number is called proton number. It is always the whole number and it ranges from 1 to 118, according to the number of the element in the Periodic Table. This number can be really important and something essential to know, in relation to a certain chemical element which is the issue of our interest at the moment.

Why is this so? Why is the atomic number so important? First of all, it is the number that makes elements different from one another as it shows the number of protons in their nuclei. Also, knowing the atomic number of an element can give us an idea about the position of the element in the Periodic Table. Atomic number of an element never changes: for example, the atomic number of oxygen is always 8, and the atomic number of Chlorine is always 18. The atomic number is marked with the symbol Z, taken from a German word zahl (or atomzahl, which is 'atomic number' in German).
This website is created for those who need to know the atomic number of a central chemical element. By using our website, you can do it in just one click and receive short and correct information on this matter. There is also some extra summary on every each chemical element which can be found at our website, including the atomic weight of each element, as well as physical and chemical properties of every element and its importance. Use this website at any time when you need to get fast and precise information about atomic or proton number of chemical elements.
List of chemical elements in periodic table with atomic number, chemical symbol and atomic weight. You can sort the elements by clicking on the table headers. Please click on the element name for complete list of element properties.
| Atomic Number | Chemical Symbol | Element Name | Atomic Weight (u) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | H | Hydrogen | 1.008 |
| 2 | He | Helium | 4.003 |
| 3 | Li | Lithium | 6.94 |
| 4 | Be | Beryllium | 9.012 |
| 5 | B | Boron | 10.81 |
| 6 | C | Carbon | 12.011 |
| 7 | N | Nitrogen | 14.007 |
| 8 | O | Oxygen | 15.999 |
| 9 | F | Fluorine | 18.998 |
| 10 | Ne | Neon | 20.18 |
| 11 | Na | Sodium | 22.99 |
| 12 | Mg | Magnesium | 24.305 |
| 13 | Al | Aluminium | 26.982 |
| 14 | Si | Silicon | 28.085 |
| 15 | P | Phosphorus | 30.974 |
| 16 | S | Sulfur | 32.06 |
| 17 | Cl | Chlorine | 35.45 |
| 18 | Ar | Argon | 39.948 |
| 19 | K | Potassium | 39.098 |
| 20 | Ca | Calcium | 40.078 |
| 21 | Sc | Scandium | 44.956 |
| 22 | Ti | Titanium | 47.867 |
| 23 | V | Vanadium | 50.942 |
| 24 | Cr | Chromium | 51.996 |
| 25 | Mn | Manganese | 54.938 |
| 26 | Fe | Iron | 55.845 |
| 27 | Co | Cobalt | 58.933 |
| 28 | Ni | Nickel | 58.693 |
| 29 | Cu | Copper | 63.546 |
| 30 | Zn | Zinc | 65.38 |
| 31 | Ga | Gallium | 69.723 |
| 32 | Ge | Germanium | 72.63 |
| 33 | As | Arsenic | 74.922 |
| 34 | Se | Selenium | 78.971 |
| 35 | Br | Bromine | 79.904 |
| 36 | Kr | Krypton | 83.798 |
| 37 | Rb | Rubidium | 85.468 |
| 38 | Sr | Strontium | 87.62 |
| 39 | Y | Yttrium | 88.906 |
| 40 | Zr | Zirconium | 91.224 |
| 41 | Nb | Niobium | 92.906 |
| 42 | Mo | Molybdenum | 95.95 |
| 43 | Tc | Technetium | 98 |
| 44 | Ru | Ruthenium | 101.07 |
| 45 | Rh | Rhodium | 102.906 |
| 46 | Pd | Palladium | 106.42 |
| 47 | Ag | Silver | 107.868 |
| 48 | Cd | Cadmium | 112.414 |
| 49 | In | Indium | 114.818 |
| 50 | Sn | Tin | 118.71 |
| 51 | Sb | Antimony | 121.76 |
| 52 | Te | Tellurium | 127.6 |
| 53 | I | Iodine | 126.904 |
| 54 | Xe | Xenon | 131.293 |
| 55 | Cs | Caesium | 132.905 |
| 56 | Ba | Barium | 137.327 |
| 57 | La | Lanthanum | 138.905 |
| 58 | Ce | Cerium | 140.116 |
| 59 | Pr | Praseodymium | 140.908 |
| 60 | Nd | Neodymium | 144.242 |
| 61 | Pm | Promethium | 145 |
| 62 | Sm | Samarium | 150.36 |
| 63 | Eu | Europium | 151.964 |
| 64 | Gd | Gadolinium | 157.25 |
| 65 | Tb | Terbium | 158.925 |
| 66 | Dy | Dysprosium | 162.5 |
| 67 | Ho | Holmium | 164.93 |
| 68 | Er | Erbium | 167.259 |
| 69 | Tm | Thulium | 168.934 |
| 70 | Yb | Ytterbium | 173.045 |
| 71 | Lu | Lutetium | 174.967 |
| 72 | Hf | Hafnium | 178.49 |
| 73 | Ta | Tantalum | 180.948 |
| 74 | W | Tungsten | 183.84 |
| 75 | Re | Rhenium | 186.207 |
| 76 | Os | Osmium | 190.23 |
| 77 | Ir | Iridium | 192.217 |
| 78 | Pt | Platinum | 195.084 |
| 79 | Au | Gold | 196.967 |
| 80 | Hg | Mercury | 200.592 |
| 81 | Tl | Thallium | 204.38 |
| 82 | Pb | Lead | 207.2 |
| 83 | Bi | Bismuth | 208.98 |
| 84 | Po | Polonium | 209 |
| 85 | At | Astatine | 210 |
| 86 | Rn | Radon | 222 |
| 87 | Fr | Francium | 223 |
| 88 | Ra | Radium | 226 |
| 89 | Ac | Actinium | 227 |
| 90 | Th | Thorium | 232.038 |
| 91 | Pa | Protactinium | 231.036 |
| 92 | U | Uranium | 238.029 |
| 93 | Np | Neptunium | 237 |
| 94 | Pu | Plutonium | 244 |
| 95 | Am | Americium | 243 |
| 96 | Cm | Curium | 247 |
| 97 | Bk | Berkelium | 247 |
| 98 | Cf | Californium | 251 |
| 99 | Es | Einsteinium | 252 |
| 100 | Fm | Fermium | 257 |
| 101 | Md | Mendelevium | 258 |
| 102 | No | Nobelium | 259 |
| 103 | Lr | Lawrencium | 266 |
| 104 | Rf | Rutherfordium | 267 |
| 105 | Db | Dubnium | 268 |
| 106 | Sg | Seaborgium | 269 |
| 107 | Bh | Bohrium | 270 |
| 108 | Hs | Hassium | 277 |
| 109 | Mt | Meitnerium | 278 |
| 110 | Ds | Darmstadtium | 281 |
| 111 | Rg | Roentgenium | 282 |
| 112 | Cn | Copernicium | 285 |
| 113 | Nh | Nihonium | 286 |
| 114 | Fl | Flerovium | 289 |
| 115 | Mc | Moscovium | 290 |
| 116 | Lv | Livermorium | 293 |
| 117 | Ts | Tennessine | 294 |
| 118 | Og | Oganesson | 294 |
Lists of Elements in Periodic Table
You can also list the elements in various ordered properties with printable tables below.

Helium Atomic Number Mass
Lists of Elements by Group Number in Periodic Table
» Group 1» Group 2» Group 3» Group 4» Group 5» Group 6» Group 7» Group 8» Group 9» Group 10» Group 11» Group 12» Group 13» Group 14» Group 15» Group 16» Group 17» Group 18Helium is a chemical element with the atomic number 2, meaning that a neutral helium atom has two protons and two electrons. The most important chemical properties of helium include its atomic mass, state of matter, boiling and melting points, and density. The element has an atomic mass of 4.0026 grams per mole and is a gas at almost all temperatures and pressure conditions. The density of helium is 0.1786 grams per liter at 32°F (0.0°C) and 101.325 kilopascals (kPa).
Liquid and solid helium can exist only in extremely low-temperature high-pressure conditions. One of the unusual properties of helium is that it cannot exist as a solid or liquid at normal pressures, even at extremely low temperatures. At a pressure of roughly 360 pounds per square inch (2.5 megapascals), the transition between liquid and solid, or the melting point, is -458°F (0.95 Kelvin). The boiling point is -452°F (4.22 Kelvin).
Some of the properties of helium make it an interesting and common subject of study in quantum mechanics. It is, because of its low atomic number, the second simplest atom after hydrogen. Mathematical procedures can be used to analyze the behaviors of the subatomic particles — protons, electrons, and neutrons — within the helium atom. Such methods cannot, however, determine the behavior of these particles with absolute certainty. Atoms with larger atomic numbers, which have more subatomic particles, tend to be harder to work with in terms of quantum mechanical analysis.
Atomic Number Helium Have
Helium is the least reactive of all of the elements. The nonreactive properties of helium arise from the fact that it is the lightest of the generally-nonreactive noble gases. A noble gas has a 'full' electron shell, meaning that it cannot easily give or receive electrons in a chemical reaction. Electron exchange or sharing is the basis for most chemical reactions, so the noble gases tend to participate in few chemical reactions. Additionally, helium has only two electrons that could participate in a reaction at all, while all of the other noble gases — and indeed, all elements aside from hydrogen — have more.
What's The Atomic Number For Helium
There are many different uses for helium that arise from the chemical properties of helium — particularly its light weight, temperature and pressure qualities, and its low reactivity. Helium is, for instance, considerably lighter than air, so it is often used to fill balloons so they can float and airships such as blimps so they can fly. Liquid helium, which can only exist at extreme pressures and at very low temperatures, is used as a coolant for superconductors, which only take on their extremely conductive properties at very low temperatures.
